Past Continuous Tense Passive Voice Active Voice

We need tenses to form a sentence and refer to a situation. Tenses help us refer to a certain time and situation. Today, we will learn all 12 tenses in English grammar we have. After each tense, you will find a video lesson explaining that tense.
What is tense in English?
The word 'tense' means 'time' in English. Every tense in English refers to a specific time that the sentence refers to. We have 12 different tenses in English:
- Simple Present tense
- Present Progressive tense
- Present Perfect tense
- Present Perfect Continuous tense
- Simple Past tense
- Past Progressive tense
- Past Perfect tense
- Past Perfect Continuous tense
- Simple Future tense
- Future Progressive tense
- Future Perfect tense
- Future Perfect Continuous tense
There are 3 main tenses (time):
- Present tense
- Past tense
- Future tense
Let's learn all 12 tenses one by one. We will start with the present tense.
SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE
The Simple Present tense, also known as the Present Indefinite tense, is used to talk about actions we do repeatedly. We use this tense to talk about repeated actions, universal facts, likes, dislikes, goals, ambitions, and a few more.
Examples:
- I teach English.
- My father goes for a walk in the morning.
- Jon wakes up at 6 am.
- Ashish listens to an English podcast before hitting the bed.
- I like talking to strangers.
- You are a great human being.
- Joanna wants to be a doctor.
- My brother doesn't like going out.
- Do you like me?
- Don't you teach yoga here?

Notice that sentences refer to actions that are repeated in the present time. The purpose of the tense is to point out the followings:
| To talk about who performs a repeated action | Jon teaches us coding. Your sister troubles me a lot. |
| To focus on what is done repeatedly (object) | Max plays football. We eat pancakes after dinner. |
| To talk about the place where something happens repeatedly | He trains in his backyard. We live in a small city. |
| To talk about the time when something happens repeatedly | I wake up at 6 am. Ashish creates content after having dinner. |
| To talk about the manner in which something happens repeatedly | Ashish teaches English amazingly well. Sometimes, Jyoti acts like a kid. |
Simple Present tense (passive voice)
In the passive voice of the Present Indefinite tense, sentences are formed using the subject (the receiver of the action) followed by is/am/are + past participle (V3). Here's the structure:
Subject (the object) + is/am/are + V3 + (by + the doer)
Notice that the object in the active voice becomes the subject in the passive voice as it is what the writer focuses on in the passive voice.
- Active: PeoplespeakEnglish around the world.
- Passive: Englishis spoken around the world (by people).
- Active: My parentstakecare of these kids.
- Passive: These kidsare taken care of by my parents.
- Active:Doeshecallyou baby?
- Passive:Areyoucalledbaby by him?
- Active: Whocallsyou every night?
- Passive: Whoare youcalledby every night?
NOTE : in the passive voice, the doer of the action (generally in most cases) is not mentioned in the sentence as it is not what the focus is on; a sentence in the passive voice focuses on the receiver of the action (someone/something that the action is done upon). But you can always add the doer of the action if you want to or if it's required.
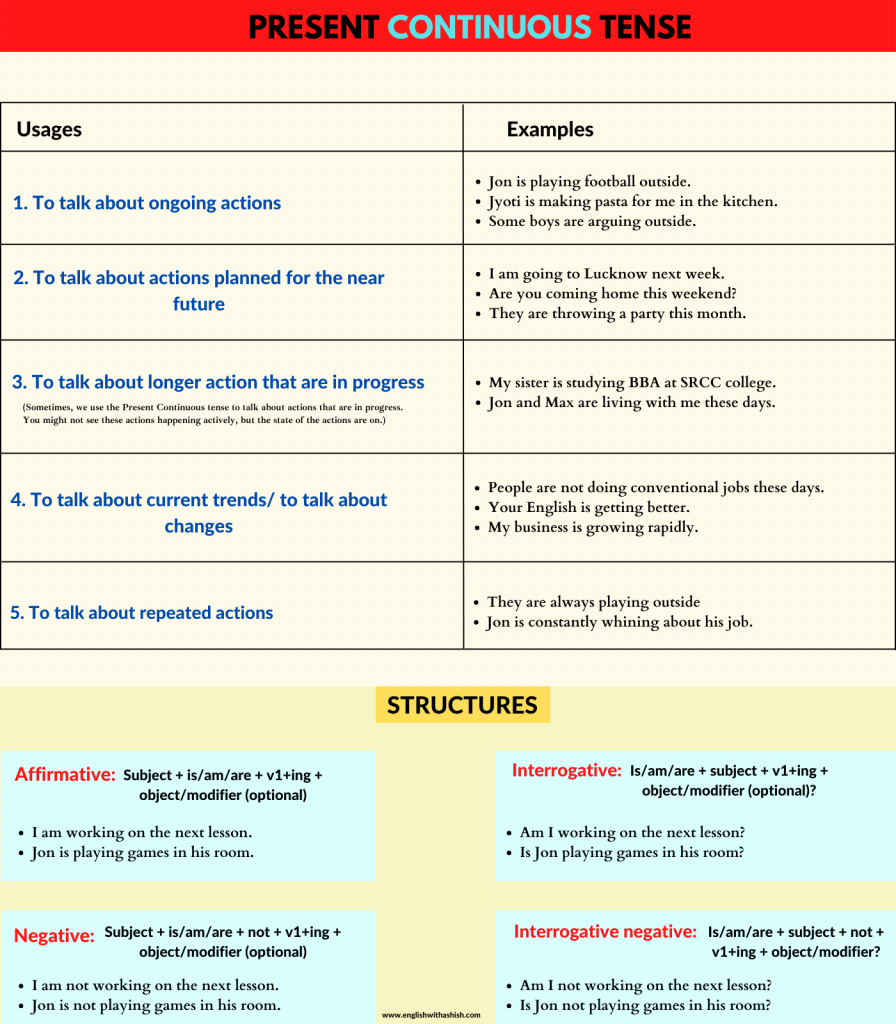
PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
The Present Continuous tense, also known as the Present Progressive tense, is a verb tense that is used to refer to actions that are going on in the present.
If I asked you to tell me what's happening there right now, you would tell me everything using the Present Continuous tense. Let me tell you what's happening here right now:
- My brotheris talking to someone over the phone.
- Some kids are playingoutside.
- Jane, my cousin,is watching T.V.
- My parentsare having coffee.
- A guy is standing next to a car.
- Some ladiesare buying something from a street vendor.
- Jimmy, my dog,is drinkingwater.
WH Interrogative sentences
Structure : WH words + is/am/are + subject + present participle (v1+ing) + object/modifier?
| TIME | When are leaving for the party? When is he coming here? |
| PLACE | Where are they hiding? Where is your father working these days? |
| REASON | Why are they fighting with each other? Why am I even talking to you? |
| MANNER | How is he doing it? How are you getting these contracts? |
| SUBJECT (doer of the action) | Who is calling you outside? Who is sitting in your car? |
| SUBJECT (doer of the action: a thing) | What is troubling you? What is bothering them? |
| OBJECT (receiver of the action) | Who/whom are you playing with? Who is he teaching English? |
| OBJECT (receiver of the action: a thing) | What are you talking about? What is the kid playing with? |
Present Continuous tense (passive voice)
In the active voice of the Present Continuous tense, we focus on the person who is doing an action currently in the present.
In the passive voice of the Present continuous tense, we focus on the object (the receiver of the action) that is receiving the action in the present. The verb tense is formed using"is/am/are + being + V3."
Active voice: Subject (doer) + is/am/are + V1+ing + object
Passive voice: The object (receiver of the action) + is/am/are + being + V3 + (by the doer)
Examples:
- Active voice: They are making a movie about me.
- Passive voice: A movie about me is being made (by them).
- Active voice: They are taking interviews for different posts.
- Passive voice: Interviews are being taken for different posts (by them).
- Active voice: The police are interrogating him right now.
- Passive voice: He is being interrogated (by the police) right now.
- Active voice: Everyone is praising your work.
- Passive voice: Your work is being praised by everyone.
PRESENT PERFECT TENSE
The Present Perfect tense is a verb tense that is used to refer to actions that occurred in the past but are important and relevant to the present. It is mainly used to talk about the status of an action or share life experiences.
Examples:
- I have completed the project.
- Maxwell has left England for the match.
- My father has helped a lot of people.
- We have never had meat.
- The boss has canceled the meeting.
- Jon has just left for office.

WH Interrogative sentences
| TIME | N.A (we don't refer to the time of the action here) |
| PLACE | Where have you worked? Where has she studied? |
| REASON | Why have you accepted their offer? Why has she come back from London? |
| MANNER | How have you done this? How has she pulled it off? |
| SUBJECT (doer of the action) | Who has asked you to come here? Who has won the competition? |
| SUBJECT (doer of the action: a thing) | N.A |
| OBJECT (receiver of the action) | Who/whom have you called? Who have you brought yourself with? |
| OBJECT (receiver of the action: a thing) | What have you bought from the market? What has she done about the case? |
Present Perfect tense (passive voice)
| Active voice | Subject + has/have + past participle (V3) + object |
| Passive voice | Object + has/have + been + past participle (V3) + (by + subject) |
Active: She has cooked the food.
Passive: The food has been cooked by her.
Both the above sentences are in the Present perfect tense and render the same meaning. But they are focusing on different things.
The first sentence, which is in the active voice, focuses on the doer of the action (subject):she. But the second sentence, which is in the passive voice, focuses on the receiver of the action (object): the food.
In the passive voice of the present perfect tense, we talk about what has been completed or finished; who has finished it is not important in the passive voice of the present perfect tense.
Examples:
- Active voice: I have written an amazing song.
- Passive voice: An amazing songhas been written (by me).
- Active voice: Jonhas helped me a lot.
- Passive voice: I have been helped a lot (by Jon).
- Active voice: Most peoplehave tried alcohol.
- Passive voice: Alcoholhas been tried (by most people).
- Active voice: Have you finished the project?
- Passive voice: Has the project been finished?
- Active voice: Has Jyoti invited you to the party?
- Passive voice: Have you been invited to the party by Jyoti?
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
The Present Perfect Continuous tense is used to talk about actions that started in the past and are still continuing in the present. The whole purpose of using the Present Perfect Continuous tense is to focus on either of the following two things:
- The time durationfor which the action has been continuing.
- The starting point of the action since when the action has been going on.
We use FOR to talk about the time duration, and SINCE is used to talk about the starting point of the ongoing action.
Let's note that we, here in the Present Perfect Continuous tense,don't just focus on the continuity of the action, we focus either on thetime duration or thestarting point of the ongoing action. If we just wanted to focus on the continuity of the action in the present, we would simply use the Present Continuous tense, not the Present Perfect continuous tense.

SIMPLE PAST TENSE
The Past Indefinite tense, also known as theSimple Past tense, is used to talk about actions that occurred in the past at a specific time.
Always remember, the time of the action, if not already understood, needs to be mentioned as this is an important facet of the Past Indefinite tense.
Past time markers: yesterday, last night, last week, last month, last year, last summer, last season, last decade, last quarter, last night, that day, that night, etc.
Examples:
- Iwokeup at 5 am.
- Jimdiedin a car accident last year.
- Wewentto see him yesterday.
- Hesaida lot of mean things to me in that meeting.

Simple Past tense (passive voice)
We use the passive voice in the Simple Past tense when we want to focus on whom or what the action was acted upon in the past, not who performed the action. With changing the voice from active to passive, the sentence structure also changes.
- They never invited me to their houses.(Active voice)
- I was never invited to their houses by them .(Passive voice)
Note that in the active voice, the focus of the sentence is on the doer of the action: who performed the action (They). But in the passive voice, the focus has shifted to the receiver of the action: the object (me). Notice that we have added the doer (the original subject) of the action in the passive voice by using the preposition 'by' and changed it to an objective pronoun (Them) from a subjective pronoun (Them). It is not mandatory to do that at all; we generally don't talk about the doer of the action in the passive voice.
| Active voice: | subject (doer) +V2 (past form) + object |
| Passive voice: | subject +was/were + past participle (V3) + by + the doer (optional) |
Examples:
- Active: Sheslappedme in front of everyone.
- Passive: Iwas slapped in front of everyone (by her).
- Active: The policearrestedthe thieves last week.
- Passive: The thieveswere arrested last week (by the police).
- Active: Most people didn't like his movies.
- Passive: His movieswere not liked by most people.
- Active:Didtheytakehim to the hospital?
- Passive:Washetakento the hospital (by them)?
PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE
We use the Past Continuous tense when we want to talk about what was happening at a particular time in the past.
Examples:
- Shewas calling me an hour ago.
- My friendswere talking about you last night.
- Wereyousleepingin the exam room?
- I was having dinner when you called.

Past continuous tense (passive voice)
The passive voice of Past continuous tense is used when you want to focus on the person or the thing that was receiving the action in the past; that was being acted upon. When the receiver of the action (object of the verb) is more important than the doer itself, write the sentence in the passive voice of Past continuous tense.
| Active voice: | subject (doer) +was/were + present participle (V1+ing)+ object |
| Passive voice: | object +was/were + being + past participle (V3) + by + subject (optional) |
- Active: I was training Megha yesterday.
(focusing on the doer of the action 'I')
- Passive: Megha was being trained (by me) yesterday.
(focusing on the object that was receiving the action 'Megha')
Examples:
- Active: I was taking the class at that time.
- Passive: The class was being taken at that time (by me).
- Active: He was eating dinner at 9 pm.
- Passive: Dinner was being eaten at 9 pm by him.
- Active: We were not recording the video.
- Passive: The video was not being recorded by us.
- Active: Was he not helping you?
- Passive: Were you not being helped by him?
PAST PERFECT TENSE
The Past Perfect tense is formed using the past tense of the auxiliary verb "to have" (HAD) and the past participle of the main verb.
Examples:
- Ihad left the party before she arrived.
- The teacherhad ended the class before we took the notes.
- The police had arrested the man.

Past Perfect tense (passive voice)
Sentences are written in Past perfect passive voice when we want to focus on the receiver of the action: when we want to talk about what or whom the doer of the action had acted upon.
| Active voice: | Subject | had | V3 | object |
| Passive voice: | object | had + been | V3 | (by + subject) |
Active: They had copied all my answers.
Passive: All my answers had been copied (by them).
Active: Someone had stolen my car before I reached home.
Passive: My car had been stolen (by someone) before I reached home.
Active: We had not recorded the video.
Passive: The video had not been recorded (by us).
Active: Had they contacted you for the class?
Passive: Had you been contacted for the class by them?
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
We use the Past Perfect Continuous tense to talk about an action that started in the past, continued for some time, and stopped before a particular time in the past.
Structure: subject +had been + V1+ing + time reference
Time reference:
- UseFORto talk about the time duration of the action.
- And use SINCE to talk about the starting point of the action.
Examples:
- We had been waiting there for 2 hours before the bus arrived.
(We started waiting in the past at some point in time and kept waiting for 2 hours. This action stopped before a particular time:the arrival of the bus)
- She had been studying English since the morning when I called.
(This action of studying started in the past at a particular time (the morning) and kept going on until a particular time:me calling)

SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE
We use the Simple Future tense, also known as the future indefinite tense, to talk about something (an action) that occurs at a certain time in the future. The word that refers to the future time is called the future time marker . The time sometimes is not mentioned as the speaker themselves don't know the time.
Some future time markers: tomorrow, next day, next week, next month, next quarter, next year, next decade…
Examples:
- The playerswill not showup today.
- Shewill cook in the evening.
- Iwill bethere in 50 minutes.
- You will pass the test.

Contractions
- I will = I'll
- You will = you'll
- We will = we'll
- He will = he'll
- She will = she'll
- It will = it'll
- They will = they'll
- Will not = won't
Future Indefinite tense (passive voice)
A sentence is formed in the Future Indefinite passive voice when the emphasis is given on the receiver of an action, rather than who does it.
| Active voice: | Subject | will | V1 | object |
| Passive voice: | object | will be | V3 | (by + subject) |
| Active voice | Passive voice |
| I will complete the task. | The task will be completed (by me). |
| We will arrange the party in an hour. | The party will be arranged in an hour. |
| The company will not hire you. | You won't be hired. |
FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE
The Future Continuous tense, also known as the Future Progressive tense, is a verb tense that is used to refer to actions happening at a certain time in the future. Note that we, here in this tense, just focus on the continuity of the action, not on when it will start or end.
Examples:
- Wewill be sleeping when we come back.
- Iwill not be doinganything after the class. I have nothing to do.
- At 12 o'clock tomorrow, Iwill be havinglunch with Tina by the lake.

FUTURE PERFECT TENSE
The Future Perfect tense is used to refer to an action that will be completed before a certain time in the future. The whole point of using this tense is to focus on the fact that the action will have ended before some point in time in the future.
I will have left my place by the time Rahul comes.
Let's say Rahul comes home at 10 pm. The action (leaving) will have taken place before this time, and this is what the sentence focuses on. The focus is on the fact that the action of leaving will have taken place before a certain time in the future.
My father will have slept before the match starts.
The action of sleeping will be completed before a certain time, which is starting of the match.

Future Perfect tense (passive voice)
| Active voice: | Subject | will have | V3 | object |
| Passive voice: | object | will have + been | V3 | (by + subject) |
Active: The company will have fired Jon before the end of the year.
Passive: Jon will have been fired before the end of the year (by the company).
Active: The government will have closed these schools.
Passive: These schools will have been closed (by the government).
Active: I will have sold this house before 2025.
Passive: This house will have been sold before 2025 (by me).
FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
The Future Perfect Continuous tense is used to refer to an action or a situation that will have been continuing for some time at a certain time in the future or before a certain time or action in the future.

Related posts:
- Subject and its types in English
- Direct and Indirect objects
- Types of complements
- Parts of a sentence
Hope you enjoyed reading the post. Do share it with others to help them and leave your questions, doubts and feedbacks in the comment section below.
Source: https://www.englishwithashish.com/all-12-tenses-in-english-grammar/
Post a Comment for "Past Continuous Tense Passive Voice Active Voice"